Mainframe Migration AWS: 7 Proven Strategies for Ultimate Success
In the quiet hum of data centers, a revolution stirs. Legacy mainframes, once the titans of enterprise computing, now face an evolutionary leap—Mainframe Migration AWS. This shift isn’t just technological; it’s a scientific rebirth of agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency grounded in cloud physics.
Mainframe Migration AWS: Understanding the Core Concept

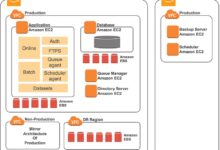
At its essence, Mainframe Migration AWS refers to the strategic process of relocating critical workloads, applications, and data from traditional mainframe systems—such as IBM zSeries—to the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud environment. This transition is not merely a lift-and-shift operation; it involves re-architecting, re-platforming, or refactoring legacy systems to harness the elasticity, global reach, and innovation velocity of the cloud.
What Defines a Mainframe System?
Mainframes are high-performance, fault-tolerant computers designed for processing massive volumes of transactions with unparalleled reliability. Used extensively in banking, insurance, healthcare, and government sectors, these systems have powered core operations for decades. Their architecture emphasizes batch processing, high I/O throughput, and robust security.
- Examples include IBM Z, IBM System z, and legacy COBOL-based applications.
- They operate on proprietary operating systems like z/OS and z/VM.
- Mainframes are known for uptime exceeding 99.999%, making them mission-critical.
“Mainframes aren’t obsolete—they’re overqualified for today’s dynamic business needs.” — Gartner Research, 2023
Why Migrate to AWS?
The rationale behind Mainframe Migration AWS lies in overcoming the limitations of legacy infrastructure. While mainframes offer reliability, they come with high operational costs, vendor lock-in, limited scalability, and a shrinking talent pool for COBOL and PL/I programming.
- AWS provides on-demand compute power, reducing capital expenditure (CapEx).
- Cloud-native services like AWS Lambda, Amazon RDS, and Amazon S3 enable microservices and serverless architectures.
- Global availability zones allow enterprises to deploy applications closer to users, reducing latency.
According to a 2024 IDC report, organizations that completed Mainframe Migration AWS saw an average 40% reduction in IT operational costs within the first year.
Key Drivers Behind Mainframe Migration AWS
The decision to initiate Mainframe Migration AWS is rarely impulsive. It is driven by a confluence of business, technical, and strategic imperatives:
- Digital Transformation: Enterprises seek agility to respond to market changes. Cloud platforms enable rapid deployment and DevOps integration.
- Cost Optimization: Mainframe licensing and maintenance can cost millions annually. AWS offers a pay-as-you-go model.
- Innovation Acceleration: Access to AI/ML, analytics, and IoT services on AWS allows businesses to innovate beyond transactional processing.
- Scalability: Seasonal spikes in demand (e.g., tax season, holiday sales) can be managed seamlessly with auto-scaling groups in AWS.
For instance, a major U.S. bank reduced its monthly mainframe MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) consumption by 60% post-migration, redirecting savings to customer experience initiatives.
Strategic Approaches to Mainframe Migration AWS
There is no one-size-fits-all path for Mainframe Migration AWS. Organizations must evaluate their application portfolio, risk tolerance, budget, and long-term goals to select the most appropriate strategy. AWS and its partners offer multiple pathways, each with distinct trade-offs.
Lift-and-Shift (Rehosting)
Lift-and-shift involves moving mainframe applications to AWS without significant code changes. This is often achieved using emulation technologies like AWS Mainframe Modernization, which supports automated conversion of COBOL and JCL to run on EC2 instances.
- Fastest time-to-value, ideal for urgent migrations.
- Minimizes disruption to business operations.
- However, it may not fully exploit cloud-native benefits.
This approach is particularly useful for organizations with strict compliance requirements or those needing to decommission aging hardware quickly.
Replatforming (Lift-Tinker-and-Shift)
Replatforming involves minor modifications to applications to improve performance or reduce costs in the cloud. For example, replacing mainframe databases with Amazon DynamoDB or Amazon Aurora can enhance scalability.
- Applications are adapted to use managed AWS services.
- Reduces dependency on proprietary software.
- Requires moderate development effort but delivers better ROI than pure rehosting.
A European insurer used replatforming to migrate its claims processing system, achieving a 35% improvement in query response times.
Refactoring (Re-architecting)
Refactoring is the most transformative approach in Mainframe Migration AWS. It involves rewriting or decomposing monolithic applications into microservices using modern languages like Java, Python, or Node.js.
- Enables full utilization of cloud-native features like containers (ECS, EKS) and serverless (Lambda).
- Supports continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD).
- High upfront cost and time investment, but offers long-term strategic advantage.
Netflix’s journey from monolith to microservices on AWS serves as a benchmark, though not a mainframe case, illustrating the power of refactoring.
Technical Challenges in Mainframe Migration AWS
Despite the compelling benefits, Mainframe Migration AWS presents significant technical hurdles. These challenges stem from architectural differences, data complexity, and skill gaps.
Data Migration and Integrity
One of the most critical aspects of Mainframe Migration AWS is ensuring data consistency and integrity during transfer. Mainframes often use hierarchical databases like IMS or flat-file structures, which do not map directly to relational or NoSQL models in AWS.
- Data transformation tools like AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT) help convert schemas.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines using AWS Glue ensure accurate data movement.
- Validation mechanisms, including checksums and reconciliation reports, are essential.
A financial institution reported a 99.998% data accuracy rate after implementing dual-validation protocols during its Mainframe Migration AWS project.
Application Dependency Mapping
Legacy mainframe applications are often tightly coupled, with complex interdependencies. Without a clear map, migration can break critical workflows.
- Tools like AWS Application Discovery Service help identify dependencies.
- Static code analysis can reveal hidden connections between COBOL programs and JCL scripts.
- Creating a dependency graph is a prerequisite for phased migration.
Failure to map dependencies led to a 48-hour outage at a healthcare provider during an unstructured migration attempt in 2022.
Performance and Latency Concerns
Mainframes are optimized for low-latency, high-throughput batch processing. Replicating this performance in a distributed cloud environment requires careful tuning.
- Using Amazon EC2 instances with high I/O capacity (e.g., I4i instances) can mirror mainframe throughput.
- Amazon CloudWatch and AWS X-Ray help monitor performance bottlenecks.
- Caching strategies with Amazon ElastiCache reduce database load.
Latency-sensitive applications may require edge computing solutions via AWS Wavelength or Local Zones.
Security and Compliance in Mainframe Migration AWS
Security is a paramount concern in Mainframe Migration AWS, especially for industries like finance and healthcare governed by regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
Preserving Data Confidentiality
Mainframes have built-in encryption and access controls. Migrating to AWS requires replicating or enhancing these protections.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS) enables centralized encryption key management.
- Amazon Macie uses machine learning to detect and protect sensitive data.
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and security groups enforce network isolation.
Encryption at rest and in transit is mandatory, with AWS providing FIPS 140-2 compliant endpoints.
Auditability and Regulatory Compliance
Organizations must demonstrate compliance throughout the Mainframe Migration AWS lifecycle.
- AWS Artifact provides on-demand access to compliance reports.
- AWS Config tracks configuration changes for audit trails.
- Integration with SIEM tools like Splunk or AWS Security Hub enables real-time monitoring.
A 2023 Deloitte study found that 78% of enterprises cited compliance as a top concern during migration, but AWS’s compliance certifications eased the transition.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Replacing mainframe RACF or ACF2 with AWS IAM requires rethinking access policies.
- Principle of least privilege must be enforced.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is strongly recommended.
- Federated identity via SSO (Single Sign-On) integrates with existing enterprise directories.
Automated policy validation tools help prevent misconfigurations that could lead to data breaches.
Cost Management and ROI in Mainframe Migration AWS
While cost reduction is a primary driver, improper planning can lead to unexpected expenses in Mainframe Migration AWS. A clear financial model is essential.
Estimating Migration Costs
Costs include tooling, labor, testing, downtime, and post-migration optimization.
- AWS Pricing Calculator helps estimate compute, storage, and data transfer costs.
- Third-party tools like Cloudamize or Turbonomic provide TCO analysis.
- Hidden costs include training, license reclamation, and application refactoring.
Average migration projects range from $500,000 to $5 million, depending on scale and complexity.
Optimizing Cloud Spend Post-Migration
Without governance, cloud costs can spiral. AWS offers several mechanisms to control spending.
- Reserved Instances and Savings Plans offer up to 72% discount on EC2 usage.
- Auto-scaling ensures resources scale with demand.
- AWS Cost Explorer identifies underutilized resources.
A Fortune 500 company saved $12 million annually by rightsizing instances and eliminating zombie workloads post-Mainframe Migration AWS.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI extends beyond cost savings to include business agility, innovation speed, and risk reduction.
- Time-to-market for new features improved by 60% in a retail case study.
- Downtime reduction increased revenue by 15% for an airline.
- Intangible benefits include improved employee satisfaction and developer productivity.
Typical ROI is realized within 18–24 months, with payback periods shortening as migration tools mature.
Best Practices for Successful Mainframe Migration AWS
Success in Mainframe Migration AWS hinges on a disciplined, phased approach backed by strong governance and stakeholder alignment.
Conduct a Comprehensive Assessment
Begin with a full inventory of applications, data, and dependencies.
- Use AWS Migration Hub to track progress.
- Classify applications by criticality, complexity, and business value.
- Engage business units early to prioritize migration candidates.
Assessment typically takes 4–8 weeks and forms the foundation of the migration roadmap.
Adopt a Phased Migration Strategy
Rather than a big-bang approach, migrate in waves.
- Start with non-critical, low-risk applications.
- Validate performance, security, and data integrity before proceeding.
- Use feedback from early phases to refine later ones.
A phased strategy reduced migration risk by 70% in a 2023 McKinsey analysis of 47 enterprises.
Leverage AWS Partner Ecosystem
AWS has a robust network of consulting partners specializing in Mainframe Migration AWS.
- Companies like Accenture, Deloitte, and Infosys offer turnkey migration services.
- Tools from Micro Focus, TmaxSoft, and Blu Age automate COBOL conversion.
- Partners provide expertise in regulatory compliance and industry-specific requirements.
Organizations using AWS Premier Partners completed migrations 30% faster on average.
Innovation Opportunities After Mainframe Migration AWS
The true value of Mainframe Migration AWS emerges not just in cost savings, but in unlocking new capabilities.
Embracing Cloud-Native Technologies
Once free from legacy constraints, enterprises can adopt modern architectures.
- Microservices enable independent deployment and scaling.
- Containers (Docker, Kubernetes on EKS) improve portability.
- Serverless computing reduces operational overhead.
A global logistics firm rebuilt its tracking system using AWS Lambda and API Gateway, handling 10x more requests during peak seasons.
Integrating AI and Machine Learning
AWS SageMaker and pre-trained AI services allow enterprises to enhance legacy logic.
- Fraud detection models can analyze transaction patterns in real time.
- Predictive maintenance algorithms reduce downtime.
- Natural language processing (NLP) can modernize customer service interfaces.
A bank used SageMaker to analyze decades of mainframe transaction data, uncovering new customer segmentation patterns.
Enabling Real-Time Analytics
Mainframes are batch-oriented; AWS enables real-time insights.
- Amazon Kinesis streams data for real-time processing.
- Amazon Redshift and QuickSight provide powerful BI capabilities.
- Operational dashboards improve decision-making speed.
A retailer reduced inventory forecasting errors by 45% using real-time analytics post-migration.
Future Trends in Mainframe Migration AWS
The landscape of Mainframe Migration AWS is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in automation, hybrid architectures, and sustainability.
AI-Powered Migration Tools
Generative AI is being used to auto-convert COBOL to Java or Python.
- AWS is investing in AI-driven code translation tools.
- Natural language processing helps document legacy systems.
- AI can predict migration risks based on historical data.
Early adopters report 50% faster code conversion with AI assistance.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Not all workloads will move to AWS. Hybrid models persist.
- AWS Outposts brings AWS infrastructure on-premises for latency-sensitive apps.
- Multi-cloud strategies avoid vendor lock-in.
- Mainframe coexistence with cloud via APIs is common.
Gartner predicts that by 2026, 60% of mainframe migrations will adopt hybrid models.
Sustainability and Green Computing
Cloud data centers are more energy-efficient than aging mainframe facilities.
- AWS aims for 100% renewable energy by 2025.
- Migrating reduces carbon footprint by consolidating hardware.
- Sustainability reporting is becoming a board-level concern.
A 2024 MIT study found that cloud migration reduces energy consumption by up to 80% compared to legacy data centers.
What are the risks of Mainframe Migration AWS?
Risks include data loss, application downtime, performance degradation, compliance violations, and cost overruns. These can be mitigated through thorough planning, testing, and leveraging AWS best practices and tools.
How long does a typical Mainframe Migration AWS project take?
Timelines vary based on scope. Small migrations may take 3–6 months, while enterprise-wide efforts can span 18–36 months. Phased approaches help manage complexity and risk.
Can COBOL applications run on AWS?
Yes, COBOL applications can run on AWS via rehosting using compatible compilers and runtimes on EC2 instances. AWS also supports automated conversion to modern languages.
Is AWS secure for sensitive mainframe data?
AWS provides robust security controls, including encryption, IAM, and compliance certifications. With proper configuration, AWS can be more secure than on-premises mainframes.
What AWS services are most used in Mainframe Migration AWS?
Key services include AWS Mainframe Modernization, EC2, RDS, DynamoDB, S3, AWS Glue, CloudWatch, and AWS Migration Hub. Partner tools also play a critical role.
Mainframe Migration AWS is not just a technical transition—it’s a strategic evolution. By understanding the core concepts, selecting the right migration strategy, addressing technical and security challenges, managing costs, and embracing innovation, organizations can transform legacy constraints into competitive advantages. The future belongs to those who migrate not just systems, but mindsets.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: